Organoids
Organoids

Overview
Overview
Recent strides in stem cell research have led to the development of organ-specific tissue from stem cells, particularly cerebral brain organoids. These miniature 3D cultures, derived from adult human blood, mimic the complexity of actual organs. They provide a valuable model for studying neurodevelopmental conditions like epilepsy. Although their current use in epilepsy research is limited, notable references in PubMed highlight their potential.
Ongoing advancements in organoid technology ensure reproducibility. Additionally, personalized medicine holds promise by creating organoids directly from affected individuals for drug testing, though automation is key for scalability (Reference: Kelava and Lancaster, 2016).
Recent strides in stem cell research have led to the development of organ-specific tissue from stem cells, particularly cerebral brain organoids. These miniature 3D cultures, derived from adult human blood, mimic the complexity of actual organs. They provide a valuable model for studying neurodevelopmental conditions like epilepsy. Although their current use in epilepsy research is limited, notable references in PubMed highlight their potential.
Ongoing advancements in organoid technology ensure reproducibility. Additionally, personalized medicine holds promise by creating organoids directly from affected individuals for drug testing, though automation is key for scalability (Reference: Kelava and Lancaster, 2016).
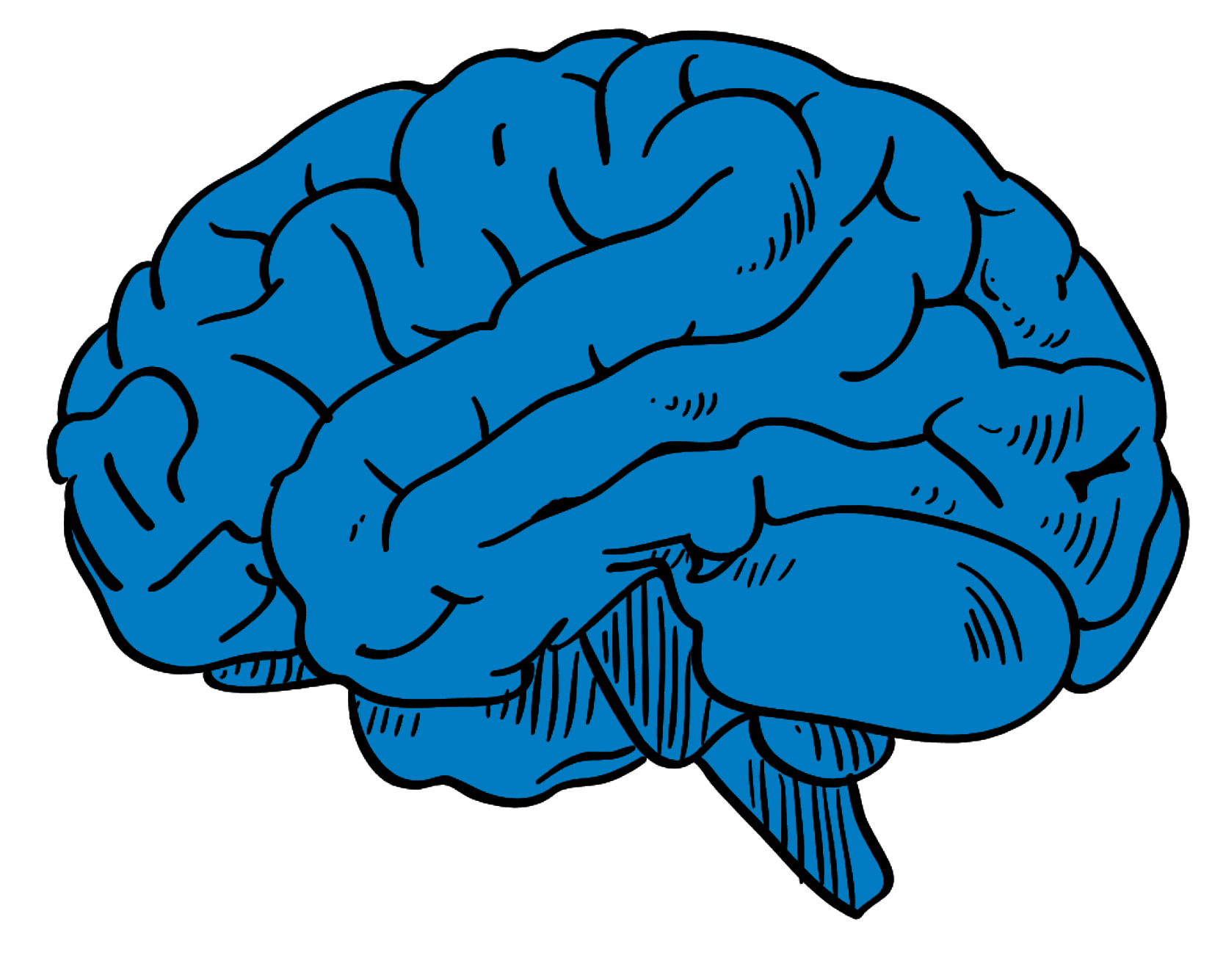
Cerebral Organoid
Cerebral Organoid
Guided Method: Unguided
Structures: Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain
Cell Types: All cell types listed above
Diseases: Machado-Joseph disease
Guided Method: Unguided
Structures: Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain
Cell Types: All cell types listed above
Diseases: Machado-Joseph disease
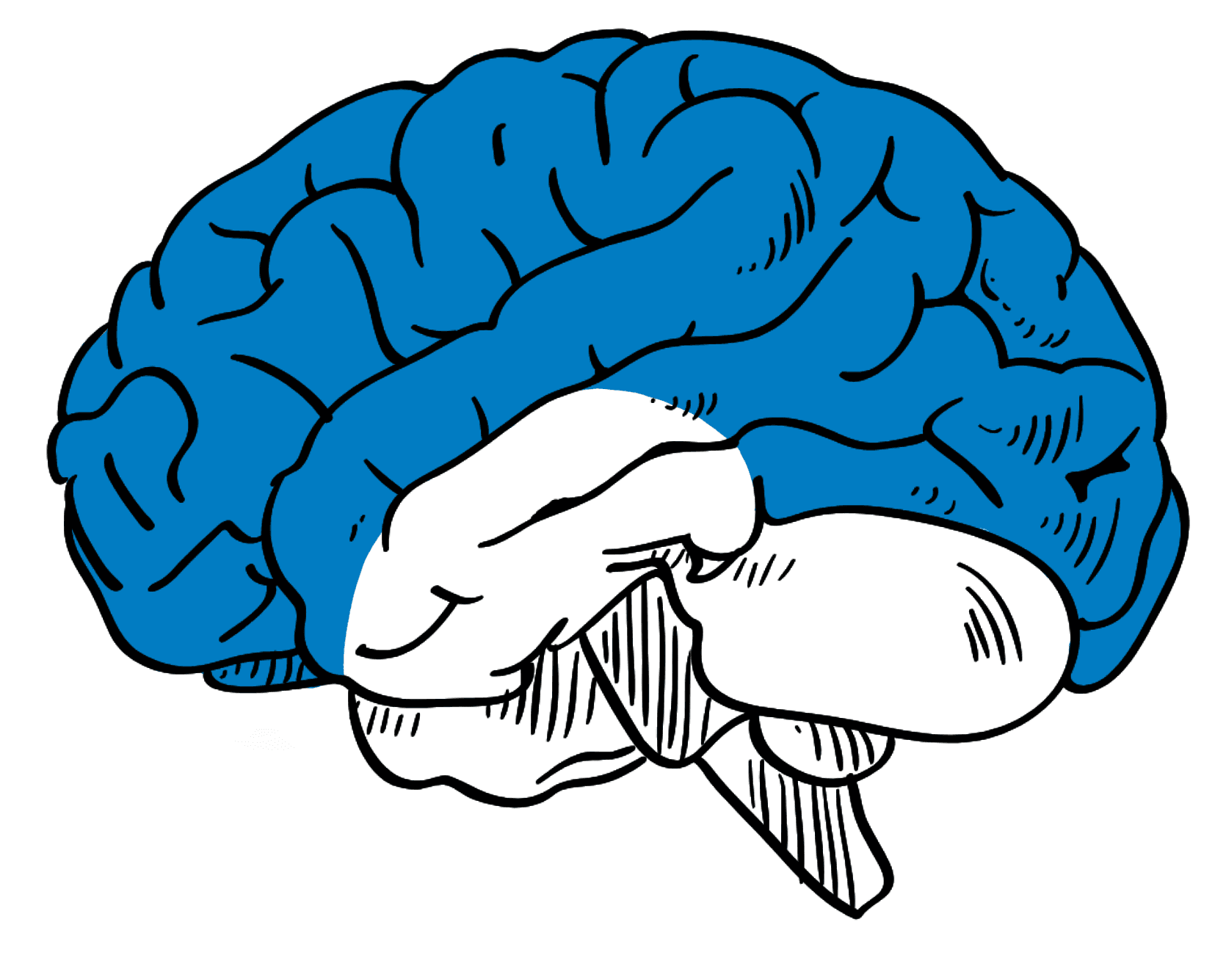
Forebrain Organoid
Forebrain Organoid
Guided Method: Guided
Structures: Cerebellum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus
Cell Types: Oligodendrocytes, Microglia, Astrocytes, basal radial glia
Diseases: Fragile X Syndrome, Alzheimers
Guided Method: Guided
Structures: Cerebellum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus
Cell Types: Oligodendrocytes, Microglia, Astrocytes, basal radial glia
Diseases: Fragile X Syndrome, Alzheimers


Cerebral Organoid
Guided Method: Unguided
Structures: Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain
Cell Types: All cell types listed above
Diseases: Machado-Joseph disease


Forebrain Organoid
Guided Method: Guided
Structures: Cerebellum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus
Cell Types: Oligodendrocytes, Microglia, Astrocytes, basal radial glia
Diseases: Fragile X Syndrome, Alzheimers
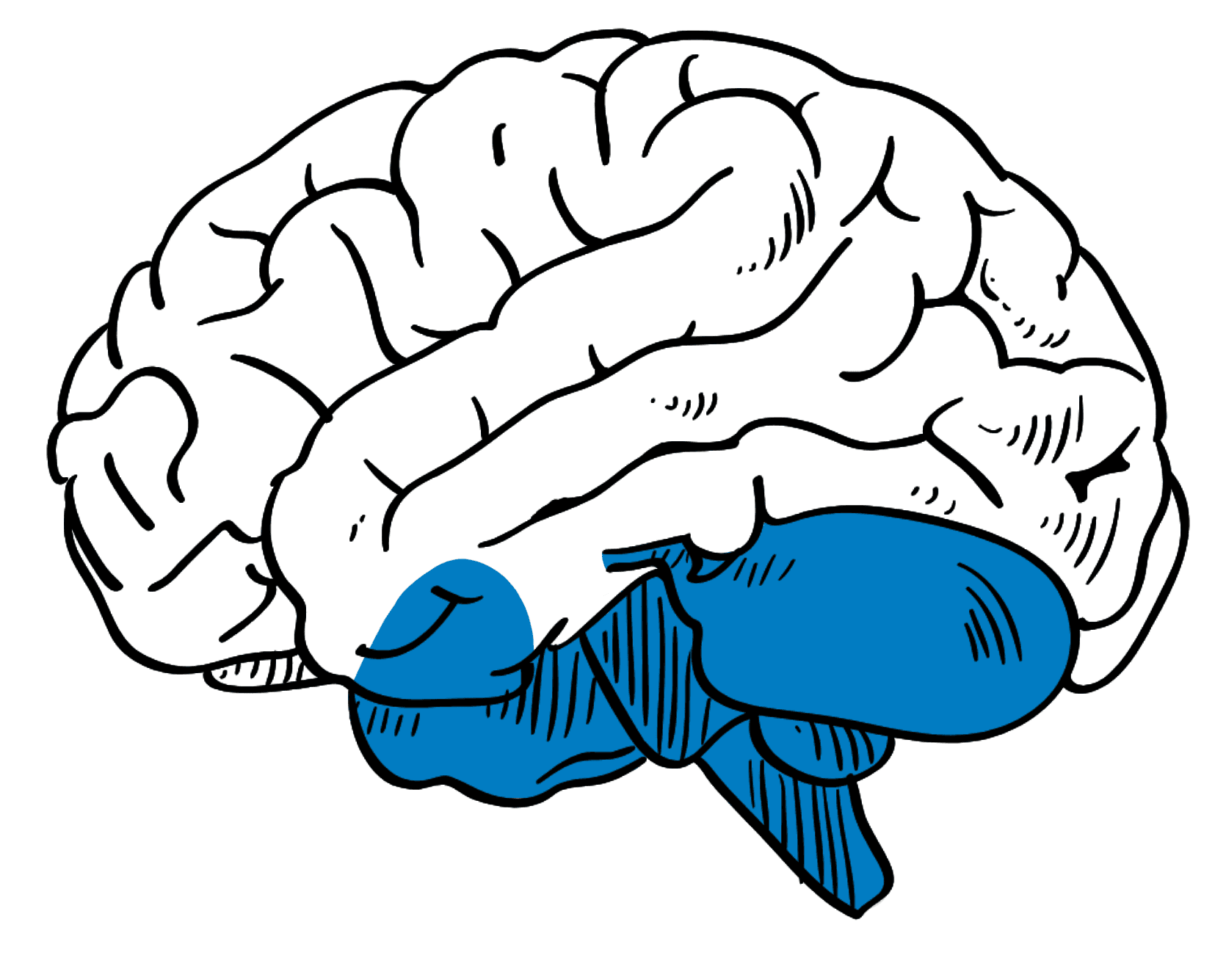

Hindbrain Organoid
Guided Method: Guided
Structures: Pons, cerebellum and medulla
Cell Types: Purkinje Cells, Granule cells
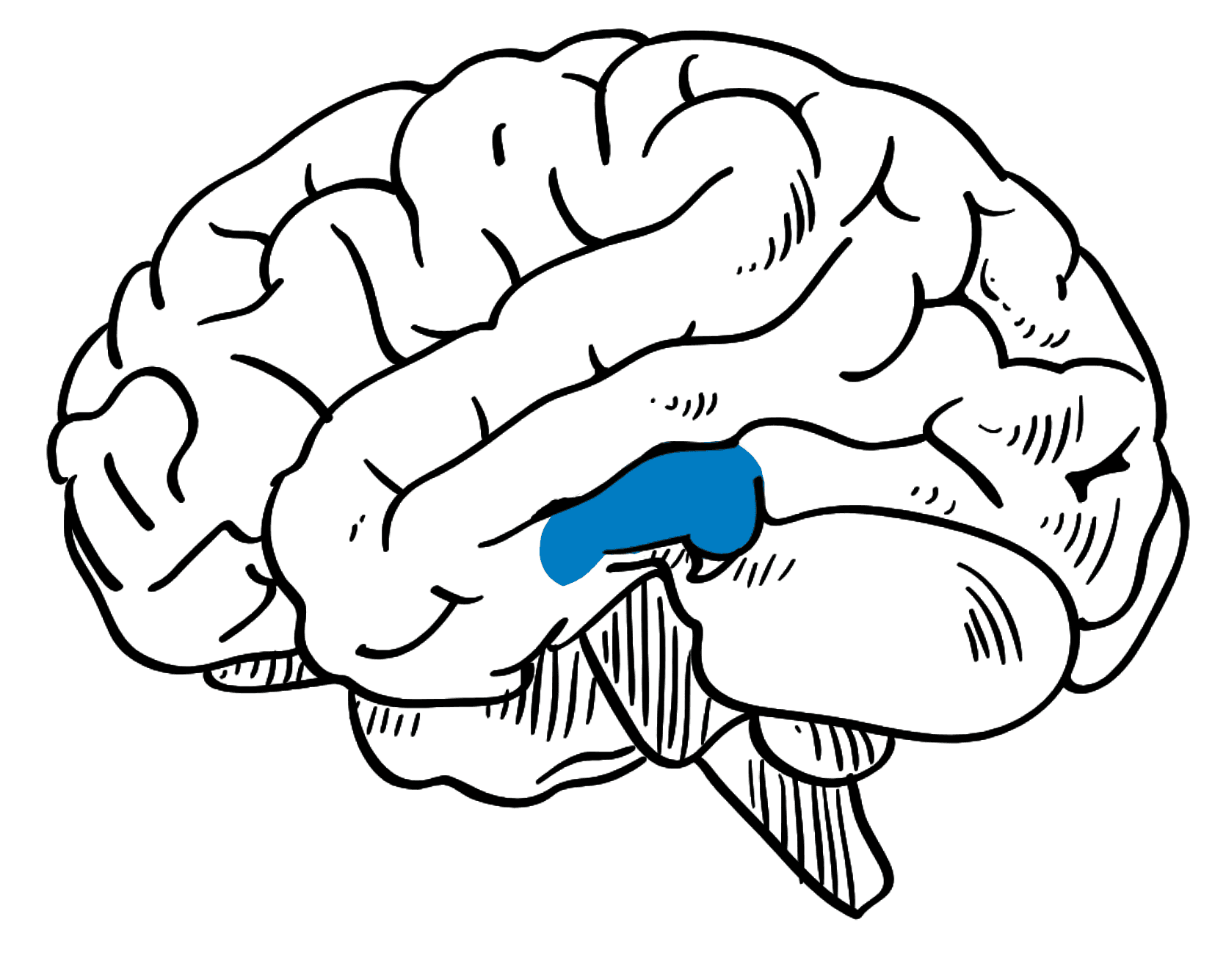

Midbrain Organoid
Guided Method: Guided
Structures: Tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, the tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles
Cell Types: Dopaminergic, GABAergic, Glutaminergic
Diseases: Parkinsons
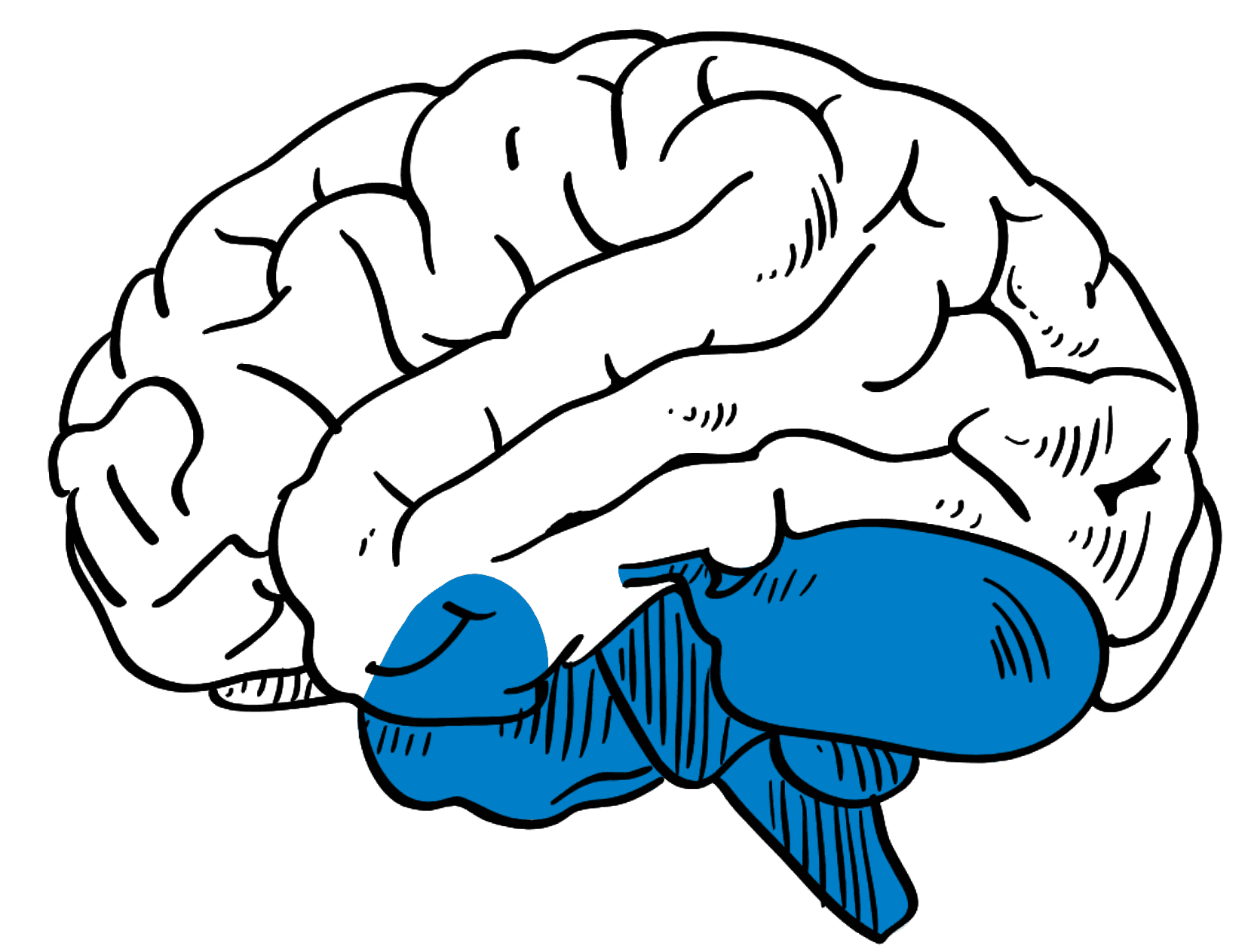

Hindbrain Organoid
Hindbrain Organoid
Guided Method: Guided
Structures: Pons, cerebellum and medulla
Cell Types: Purkinje Cells, Granule cells